Clues revealed to cause of deadly kidney disease in newborns
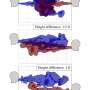
Babies born with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) often develop kidney failure because they have very large kidneys filled with tiny cysts. Even with excellent medical care, about 30% die shortly after birth. New research now provides clues into how gene defects may cause this condition, which occurs in 1 out of 20,000 newborns. The findings appear in an upcoming issue of theJournal of the American Society Nephrology(JASN), a publication of the American Society of Nephrology.
Mutations in a gene named PKHD1 cause ARPKD, but it's not clear how. Jason Bakeberg and Christopher Ward, ChB, PhD (Mayo Clinic) led a team that bred mice to have a small tag inserted into this gene. This tag allowed the researchers to follow the activities of the protein made by the gene, called fibrocystin.
"We found that small vesicles, termed exosome-like vesicles (ELVs), present in urine and other bodily fluids have abundant fibrocystin on their surface. This has allowed us to follow ELVs as they interact with primary cilia, or small hair-like structures that project into the urine from cells within the kidney's tubules," said Dr. Ward. "We believe that ELVs are involved in transporting a range of signals through urine and that ELV interactions with cilia are central to this signaling."
The findings may help investigators to understand how PKHD1 gene mutations cause ARPKD and to develop tests for the disease. "For example we are working on urine-based tests for polycystickidney diseasebased on the use of ELVs," said Dr. Ward.
Explore further