新的角膜内皮细胞系的发展为理解角膜细胞生物学提供了有力的工具
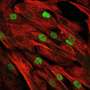
人角膜内皮细胞(HCENCs)形成一系列六角形细胞,其主要功能是通过调节角膜水合来维持角膜清晰度。由于衰老或角膜内皮疾病(例如FUCHS营养不良)导致的细胞损失可导致角膜水肿和失明,导致角膜移植的需要。
研究人类角膜内皮一直是一个难题细胞生物学家因为有限的细胞模型系统存在并具有显着的缺点。主要缺点是HCENC细胞不要分裂,这些细胞用于病人移植和实验室研究的来源有限。这个领域的研究现在比较容易。
Schepens Eye Research Institute,Mass。眼睛和耳朵,已经开发出HCENC-21和HCENC-21T,这是人角膜内皮的两种新型模型系统。他们的发现,端皮细胞永生化的端皮酶产量官能六角形单层,在线《公共科学图书馆•综合》。
由Ula Jurkunas,M.D的研究团队开发了一流的人角膜内皮模型系统。
“这些模型非常妥善了解眼睛中的组织中已知的临界特征和功能,”Jurkunas博士说。"They also fulfill essential technical requirements, e.g. indefinite number of and a high rate of cell division, to be a powerful tool. They will enable cell biologists to more reliably study human corneal endothelium in health and disease. The ability to enhance HCEnC cell self renewal and growth opens a new window of development of novel regenerative therapies for corneal swelling, hopefully reducing the need for角膜移植在未来。”
进一步探索









用户评论