Scientists discover new brain changes in early Alzheimer's disease
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have discovered new changes occurring in the human brain in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. The researchers used a multiomic approach to determine RNA, protein, and phosphorylation levels and carried out further neurobioinformatic analyses on them. The findings, drawing on data from a Finnish biobank of brain tissue samples, were published inNeurobiology of Disease.
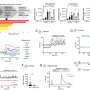
Alzheimer'sdiseaseis the most common neurodegenerative disease, which is strongly characterised by the accumulation of beta-amyloid peptide and hyperphosphorylated tauproteinin the brain tissue. In order to find new predictive biomarkers and targets of treatment for Alzheimer's disease, it is crucial to identify accumulation-induced early changes in the brain. Plenty of research has been conducted into changes occurring in the RNA expression of genes in the brain of people with Alzheimer's disease, but very few studies so far have focused on the entire proteome covering the entire set of the proteins expressed in cells.
"Yet, we know that changes in expression aren't always translated to the protein level, and we also know that phosphorylation regulates the function of the proteins produced. Therefore, it is essential to look at multiple levels of regulation at the same time in order to understand the functional changes taking place in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease," Postdoctoral Researcher Mikael Marttinen from the University of Eastern Finland explains.
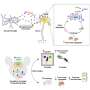
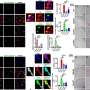
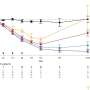
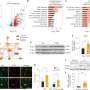
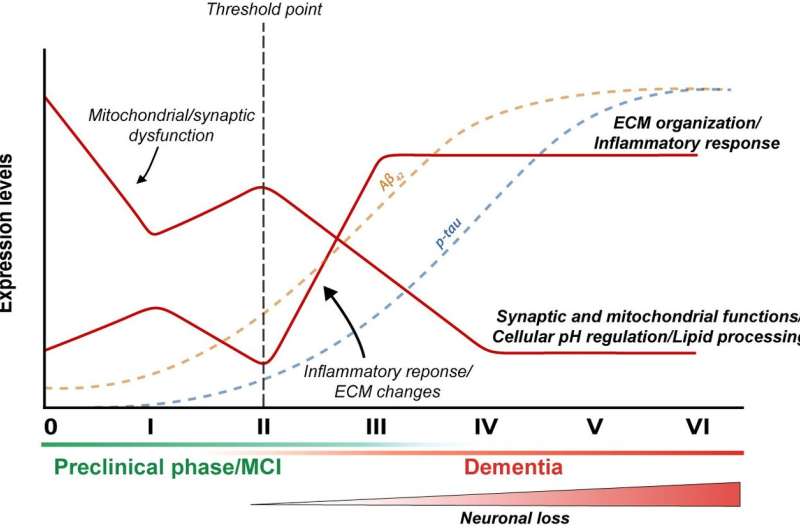
In the newly published study, researchers from the University of Eastern Finland used data available in a unique Finnish biobank ofbrain tissuesamples, where samples are categorised according to the accumulation of phosphorylated tau protein, representing the different stages of Alzheimer's disease. By carrying out genome-wide analysis of the samples for changes in RNA, proteins and protein phosphorylation, and by conducting neurobioinformatics analyses, the researchers managed to demonstrate associations of functional changes in certain brain cell types with Alzheimer's-related accumulation of phosphorylated tau protein. Theresearchersalso showed thatmachine learningcan be used to classify patients into different stages of disease pathogenesis merely by looking at changes in the expression of a selected group of genes.
Further research will focus on exploring whether the newly discovered brain changes in the different stages of the disease are also visible incerebrospinal fluidand blood samples, and whether these could also be used as new predictive biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, the changes discovered in the early stages of the disease open up new avenues for potential targets of treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
Researchers from the University of Eastern Finland have used data from the biobank of brain samples also in earlier studies, and the findings have been reported in several leading scientific journals. The new study was carried out in collaboration between the University of Eastern Finland and the UK-based Proteome Sciences Plc.
More information:Mikael Marttinen et al, A multiomic approach to characterize the temporal sequence in Alzheimer's disease-related pathology,Neurobiology of Disease(2018).DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.12.009