罕见的卵巢癌确认没有从其他地方种植
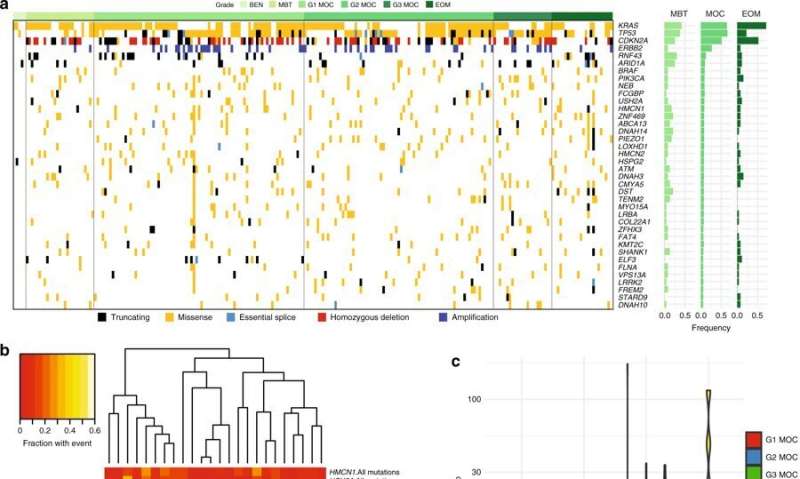 The molecular origin and taxonomy of mucinous ovarian carcinoma Variant analysis. a Summary of variants across the cohort for genes mutated in > 5% of MOC; also includes copy number alterations for CDKN2A and ERBB2. BEN, benign mucinous; MBT, borderline mucinous; MOC, mucinous ovarian carcinoma; EOM, extra-ovarian metastases. b Comparison of copy number alterations and mutations with other tumor types, summarised by frequency for each. Number of cases shown below. *Higher number is for selected genes tested by Sanger sequencing/SNP arrays (see Methods); lower number from exome analysis. c Number of variants per Mb by group (ANOVA, two-sided, F = 1.55, df = 5, p = 0.18), combining exome and targeted sequencing cohorts. d Top: number of single nucleotide variants (SNV) input to signature detection from whole exome and whole genome sequencing, with each column an MOC case. Note whole genome samples truncated at 300 (asterisk). Bottom: COSMIC mutation signatures18" width="800" height="479">
The molecular origin and taxonomy of mucinous ovarian carcinoma Variant analysis. a Summary of variants across the cohort for genes mutated in > 5% of MOC; also includes copy number alterations for CDKN2A and ERBB2. BEN, benign mucinous; MBT, borderline mucinous; MOC, mucinous ovarian carcinoma; EOM, extra-ovarian metastases. b Comparison of copy number alterations and mutations with other tumor types, summarised by frequency for each. Number of cases shown below. *Higher number is for selected genes tested by Sanger sequencing/SNP arrays (see Methods); lower number from exome analysis. c Number of variants per Mb by group (ANOVA, two-sided, F = 1.55, df = 5, p = 0.18), combining exome and targeted sequencing cohorts. d Top: number of single nucleotide variants (SNV) input to signature detection from whole exome and whole genome sequencing, with each column an MOC case. Note whole genome samples truncated at 300 (asterisk). Bottom: COSMIC mutation signatures18" width="800" height="479">
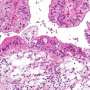
由Peter Mac领导的国际研究揭示了粘液卵巢癌(MOC)的起源,与其他类型的卵巢癌不同,这种稀有癌症不会从身体其他地方种植。
该研究提供了新的见解,可能导致MOC定制治疗,占所有人的3%卵巢癌。重要的是,研究发现MOC是真正的妇科癌症而不是在胰岛素,肠或乳房开始的癌症的远处转移。
“最近我们对卵巢癌的理解急剧发生变化,我们现在认识到卵巢可以像漫游癌细胞的海绵一样行动,”凯莉·戈德博士是彼得MAC和高级作者的癌症基因组学计划的团队领导者。
“当他们起源于其他器官,一些癌症的一些癌症经过卵巢癌,并通过识别这些癌症来自我们能够改善治疗和预防的地方。
“我们仍然有办法去寻求所有类型的卵巢癌,特别是最稀有的形式,但在MOC的情况下,我们现在确认这不是转移性肿瘤,但它在卵巢中从卵巢开始早期。”
将MoC中观察到的遗传事件与来自许多不同组织类型的其他肿瘤进行比较,并且这最终显示了MOC作为卵巢的独特癌症。良性和边缘线卵巢肿瘤也被测序,揭示这些与MOC的遗传相关,所述方式表明MOC可以从这些不那么腐蚀性肿瘤中发展。
MOC在澳大利亚每年影响少于80名女性,并且超过500种MOC样本和相关肿瘤的样本必须来自全球各地的来源,以完成这项研究。
题为“粘液卵巢癌” - 本周在网上发表的“粘液卵巢癌”的研究结果自然通信。
分析 - 涉及的国际合作并从数百种基因组中测序DNA - 还揭示了可以支持MOC定制治疗的新潜在治疗靶标。
“在我们的研究结果中建立,有一个强有力的情况,让妇女参与已在发育中的药物的临床试验中,并靶向与MOC的遗传相似性的固体肿瘤,”Gorringe也说。
这包括用KRA或TP53突变靶向癌症的药物,以及HER2扩增。
今年澳大利亚妇女约有1500名澳大利亚女性将被诊断出患有卵巢癌。最常见的高档血液癌症患者占案件的约65%。几十年而且没有量身定制的治疗,MOC已与高级浆液癌癌相同。
进一步探索







用户评论