数字化地展开海马体,以更好地了解大脑疾病
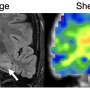
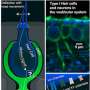
![Figure 1. Illustration of hippocampal subfield topology in traditional and multiplanar histological slices (data from [42] and segmentations from [20]). (A) Traditional hippocampal slices with and without subfields overlaid. Coronal slices through the hippocampal body (top) are the most commonly used orientation. In particular, slices through the hippocampal head (light blue broken outline) and tail (dark blue broken line) show discontiguities due to out-of-plane sampling. (B) Approximate locations of the coronal slices (outlined in unbroken or broken blue lines) are shown on the left-side 3D model of the hippocampus. A sagittal slice is shown in the full brain image on top (outlined in orange). Folds including digitations and medial curvature in the hippocampal head and tail are illustrated by the black line in the right-side 3D model. (C) Multiplanar resampled slices along the axis of hippocampal curvature with and without subfields overlaid. The color of each image outline corresponds to the location of its sampling on the right-side 3D hippocampal model in (B). The contiguity of subfields is shown by a black line and is consistent in all slices in (C) as described in classic neuroanatomy. Abbreviations: CA, cornu ammonis; DG, dentate gyrus; Sub, subiculum. Credit: DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2021.06.005 数字化地展开海马体,以更好地了解大脑疾病](https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2021/digitally-unfolding-th.jpg)
西方大学开发的一项新技术可以直观地消除大脑某个区域的皱纹和褶皱,这可能会为研究人员了解大脑疾病提供更准确的图像。
海马体是大脑的一个区域大脑经常被临床医生和研究人员用来寻找了解的线索疾病进展以及对治疗的反应脑部疾病.海马体由两个海马形状的大脑结构组成,位于大脑的中心,在记忆形成中起着重要作用。它是大脑中第一个显示出阿尔茨海默病和其他疾病损害的区域之一神经退行性疾病它与癫痫和重度抑郁症有关。
海马体的解剖结构因人而异,特别是在观察它自身折叠的方式时。
博士生乔丹·德克拉克说:“我们试图解决的基本问题是,海马体是折叠的,但它在两个人之间的折叠方式并不完全相同。”“我们采用的方法是数字化展开,这样我们就能更准确地比较患者之间的异常情况。”
该技术使用从核磁共振磁共振成像(MRI)技术以数字方式将3D褶皱重建为2D结构——本质上是将褶皱熨平。
描述这项技术前景的论文发表在该杂志上神经科学发展趋势并且是DeKraker在Ali Khan和Stefan的监督下在西方Schulich医学和牙科学院的博士工作的顶峰Köhler。
大脑与心智研究所的心理学教授、首席研究员Köhler说:“很难在一个人身上找到海马体的某一部分,也很难在另一个人身上找到相应的部分,因为这种折叠在人与人之间存在差异。”“在处理临床问题时,能够做到这一点是相关的,因为你必须考虑哪些是正常变异性的一部分,哪些是临床异常的独特之处。在这个层面上,这项技术在未来将真正有所帮助。”
该团队在研究了使用北美最强大的MRI磁体之一罗伯特研究所(Robarts Research Institute)的超高场MRI获得的患者的成像数据后,开始开发这项技术,这些数据产生了超高分辨率的大脑图像。这些图像使他们能够看到患者之间折叠模式的差异,这是低分辨率成像无法看到的。
接下来,该团队正在开发一个基于网络的应用程序,允许临床医生和研究人员输入他们的成像数据,并使用人工智能以同样的方式展开海马体。
“对于癫痫,这可能有助于提供一种高分辨率的方法,帮助外科医生确定大脑的哪个部位进行治疗、切除或植入电极,”舒利奇医学与牙科助理教授、加拿大计算神经成像研究主席、罗伯茨研究所的科学家Khan说。
对于阿尔茨海默病,它可能提供一个更敏感的标记,在疾病症状出现之前显示大脑的早期变化。对于其他神经退行性疾病或精神疾病,如重度抑郁症,它可以提供一个跟踪治疗反应的标记。
更多信息:Jordan DeKraker等,基于表面的海马亚场分割,神经科学发展趋势(2021)。DOI: 10.1016 / j.tins.2021.06.005