研究人员发现如何预测一种最广泛使用的抗乳腺癌药物的疗效
精准肿瘤学旨在指出哪种药物可能对每个特定的癌症患者都有效。目前,这些靶向疗法仅适用于5%的癌症。这项研究由CNIO研究人员Miguel a . Quintela-Fandino和Silvana Mouron与几家西班牙医院的肿瘤科一起进行,他们发现了一种方法,可以确定各种癌症常规化疗中最常用的药物之一紫杉醇是否对每位患者有效。
这项工作已发表在自然通讯.
靶向治疗主要是基于对基因突变在每种癌症中。Quintela和Mouron的研究重点是her2阴性乳腺癌,这种乳腺癌占乳腺癌诊断的85%,在大多数情况下,不是由于少数而是由于几种致癌基因突变——因此,针对这种肿瘤设计基于基因突变的靶向治疗是一个很难实现的目标。
然而,Quintela和Mouron并没有进行(基因的)基因组分析,而是(蛋白质的)蛋白质组学分析。他们在之前的研究中表明,即使存在大量的致癌基因突变,也只会出现少量的蛋白质改变。
两种蛋白质,CDK4和丝状蛋白,预测对紫杉醇的反应
换句话说,在大多数癌症中,在对特定基因没有反应的患者中没有发现共同的遗传标记药物,常见的蛋白质相关标记确实可以找到。蛋白质是执行细胞大部分功能的分子;基因(在DNA分子中)包含产生有机体所需的所有蛋白质的信息。
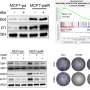
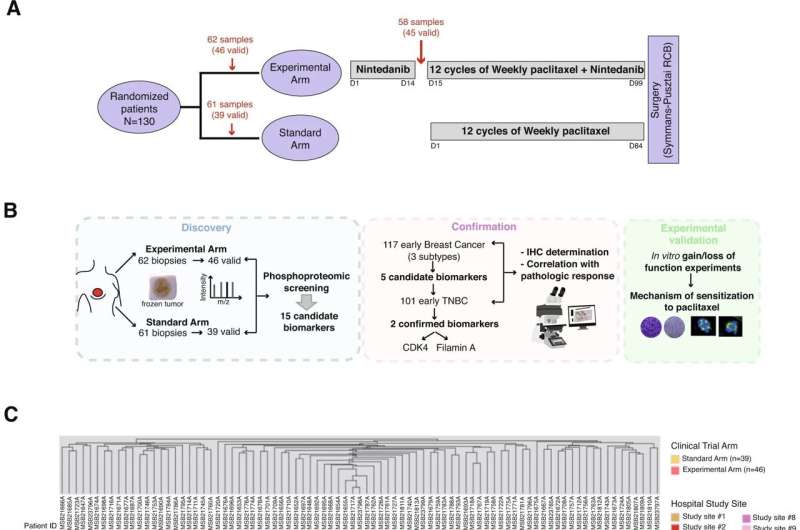
CNIO组分析her2阴性乳腺癌症来自130名接受紫杉醇治疗的患者的样本,紫杉醇是治疗乳腺癌、卵巢癌、肺癌、膀胱癌、前列腺癌、黑色素瘤、食道癌和其他癌症最广泛使用的药物之一。他们在对紫杉醇有反应的患者样本中寻找蛋白质表达的相似性,并发现了两种与紫杉醇反应特别相关的蛋白质:CDK4和丝状蛋白。
“常规化疗反应的第一个预测因素”
研究人员表明,这种关联在使用紫杉醇时出现,而在使用其他药物时则没有。
CNIO乳腺癌临床部门负责人、首席研究员Miguel a . Quintela-Fandino说:“我们发现CDK4和丝氨酸蛋白水平高的患者在90%的病例中有阳性反应率。”
“这项研究确定了传统化疗治疗的第一个特定预测因素,迄今为止,人们只知道间接或不完善的预测标记。相反,CDK4和filmanin A与紫杉醇CNIO的研究人员补充说。
这项工作不能立即应用于临床。“这一发现将被纳入肿瘤治疗武器库,流行病学和临床研究都必须实施,”Quintela-Fandino说。